Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has emerged as a pivotal treatment in modern medicine. This therapy involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment, which has been proven beneficial for a variety of health conditions.
Within the realm of HBOT, two primary types of chambers are utilized: multiplace and monoplace. This guide aims to thoroughly explore the distinctions between these two types, providing insights into their functionalities, benefits, and ideal applications.
Multiplace Chambers Explained
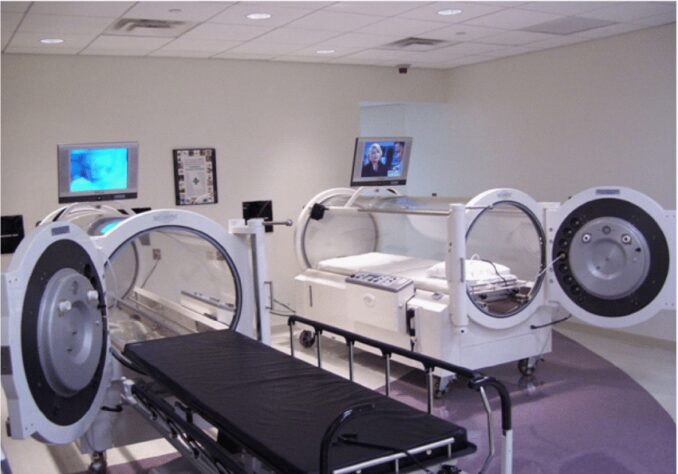
Multiplace chambers are large hyperbaric facilities designed to accommodate multiple patients simultaneously. These are sizable enough to allow medical staff to accompany patients inside, ensuring direct monitoring and care during the treatment.
- Capacity: Multiplace chambers can hold several people, ranging from two to over a dozen.
- Construction: They are typically constructed with robust materials like steel, capable of withstanding high pressures.
- Accessibility: They often have built-in seats or beds and are equipped with communication systems and viewing windows.
The Mechanics
A key aspect of multiplace chambers is their operational mechanics. Unlike monoplace ones, where patients directly breathe 100% oxygen, multiplace variations maintain a normal air environment inside.
- Oxygen Delivery: Patients in a multiplace chamber receive oxygen through masks or hoods.
- Pressure Levels: These chambers can reach higher pressure levels, making them suitable for more severe medical conditions.
- Safety Measures: Enhanced safety features are a hallmark of multiplace chambers, including fire suppression systems due to the mixture of air and oxygen.
Advantages and Ideal Uses
Multiplace chambers offer distinct advantages, particularly in terms of patient interaction and care.
- Patient Comfort and Interaction: The ability to treat multiple patients simultaneously facilitates interaction and support among them.
- Medical Supervision: The presence of medical personnel inside the chamber enhances patient safety and allows for immediate medical intervention if necessary.
- Versatility: These chambers are ideal for treating severe cases, such as decompression sickness in divers or critical infections.
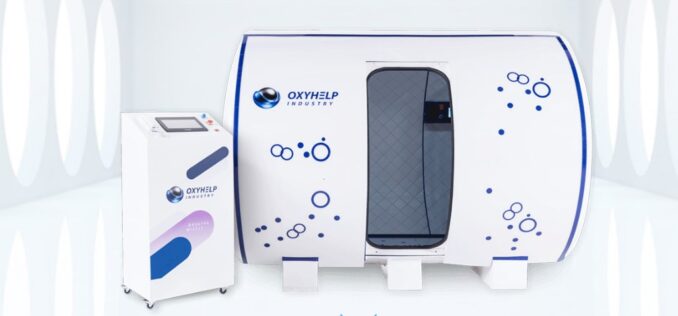
Monoplace Chambers Explained
Source: researchgate.net
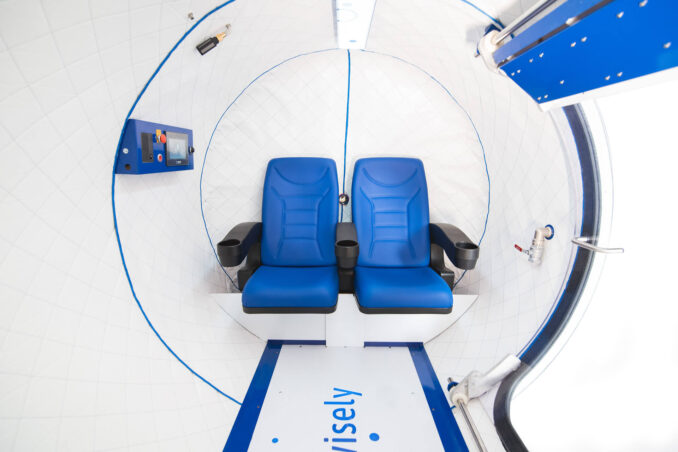
Monoplace chambers represent a more individualized approach to hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Designed for single-patient use, these chambers are more compact and function differently from their multiplace counterparts.
- Size and Design: Typically cylindrical, these chambers are smaller and cater to one person at a time.
- Material: Often made from transparent acrylic, allowing for patient monitoring from outside the chamber.
- Ease of Use: Their smaller size and simpler design make them more accessible for various healthcare settings.
The Mechanics
The operational principles of monoplace chambers are distinct from multiplace chambers, primarily in their oxygen delivery method.
- Oxygen Environment: The entire chamber is filled with 100% oxygen, eliminating the need for separate oxygen masks or hoods.
- Pressure Levels: While capable of high pressures, monoplace chambers generally operate at lower pressures compared to multiplace chambers.
- Safety Considerations: Due to the pure oxygen environment, strict safety protocols are in place to mitigate fire risks.
Advantages and Ideal Uses
Monoplace chambers have their unique set of benefits, particularly suited for certain medical conditions and settings.
- Individualized Treatment: Each session is tailored to the individual, providing personalized care.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Their smaller size makes them easier to install and maintain in various healthcare facilities.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, monoplace chambers are less expensive to operate and maintain than multiplace chambers.
Comparative Analysis
The primary distinctions between multiplace and monoplace chambers lie in their capacity, operational mechanics, and application scopes.
- Capacity and Size: Multiplace chambers can treat multiple patients, while monoplace ones are designed for individual treatment.
- Oxygen Delivery Method: Multiplace chambers use air with oxygen masks or hoods, whereas monoplace variations involve breathing pure oxygen within the entire chamber.
- Application Scope: Multiplace chambers are often used for more severe medical conditions requiring higher pressures and medical supervision, while monoplace ones are suited for more routine or individualized treatments.
Choosing the Right Chamber for Treatment
The choice between a multiplace and a monoplace chamber depends on several factors, including the medical condition being treated, the facility’s capabilities, and patient preferences.
- Medical Condition Severity: Severe cases may benefit more from the capabilities of a multiplace chamber.
- Facility Resources: The availability of space and resources can dictate the feasibility of installing and maintaining a particular type of chamber.
- Patient Comfort and Preference: Some patients may prefer the privacy and individualized attention of a monoplace chamber.
Future Prospects and Innovations in HBOT
As we progress through 2024, advancements in hyperbaric oxygen therapy continue to evolve, influencing the design and functionality of both multiplace and monoplace chambers.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in safety, comfort, and efficiency are ongoing in the realm of HBOT chambers.
- Research and Development: Ongoing research is expanding the potential applications of HBOT, potentially impacting the future design and use of these chambers.
- Accessibility and Affordability: Efforts are being made to make HBOT more accessible and affordable, potentially leading to a wider adoption of both multiplace and monoplace chambers in various healthcare settings.
Impact on Patient Recovery and Outcomes
Effectiveness in Diverse Medical Conditions
The effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen therapy, whether in a multiplace or a monoplace chamber, significantly depends on the specific medical condition being treated. Both types of chambers have demonstrated efficacy in a range of conditions, from wound healing to neurological disorders.
- Wound Healing: HBOT is known to accelerate wound healing, particularly in cases of diabetic foot ulcers and chronic wounds.
- Neurological Benefits: Research suggests positive outcomes in treating stroke, traumatic brain injury, and other neurological conditions with HBOT.
- Diving-Related Illnesses: Decompression sickness, a risk for divers, is effectively treated in multiplace chambers due to their higher pressure capabilities.
Patient Experience and Comfort
Patient experience in hyperbaric oxygen therapy varies greatly between multiplace and monoplace chambers, impacting overall comfort and satisfaction.
- Privacy and Individual Attention: Monoplace chambers offer a more private experience, which can be comforting for some patients.
- Social Interaction: In contrast, multiplace chambers allow for social interaction and mutual support among patients, which can be beneficial for mental health during treatment.
- Claustrophobia Considerations: For patients who may experience claustrophobia, the spaciousness of a multiplace chamber can be more accommodating.
Recovery Time and Efficiency
The efficiency of treatment and recovery time can also differ based on the type of hyperbaric chamber used.
- Session Duration: Treatment sessions in both chamber types typically last around 90 to 120 minutes but can vary based on the condition being treated.
- Frequency of Sessions: The total number of sessions required can vary, with some conditions necessitating daily sessions over several weeks.
- Long-Term Outcomes: The long-term effectiveness of HBOT in improving patient outcomes is an area of ongoing research, with promising results in chronic conditions.
Final Words
The world of hyperbaric oxygen therapy is diverse and complex, with multiplace and monoplace chambers offering distinct benefits and functionalities. Understanding these differences is crucial for medical professionals, patients, and healthcare administrators alike. As we move forward, the evolution of HBOT technology promises to enhance patient care and expand the possibilities of treatment, reaffirming the significance of both multiplace and monoplace chambers in modern medicine.